|
|
(Hyper) Lucent Hemithorax
Causes
- Pneumonectomy
- Initially on the side of the resection; eventually fibrosis can lead to overexpansion of the opposite side
- Pulmonary embolism
- Usually large pulmonary emboli may lead to oligemia of the affected lung (Westermark sign)
- Mucous plug
- May result in air-trapping and overaeration
- Pneumothorax
- Radical Mastectomy
- Removal of the breast and the underlying pectoralis major and minor muscles along with axillary lymph nodes; in a modified radical, the pectoralis is spared
- Poland Syndrome
- Congenital unilateral aplasia of the pectoralis muscle
- Swyer-James Syndrome
- Unilateral hyperlucent lung that usually develops during childhood as a sequela of post-infectious bronchiolitis obliterans
- Pulmonary sling
- Anomalous origin of the left pulmonary artery may obstruct the right main bronchus leading to air-trapping
- Foreign-body aspiration (Obstructive Emphysema)
- May result in over aeration of affected side due to air trapping
- Bronchial atresia
- Collateral drift leads to overexpansion
- Congenital lobar emphysema
- Usually in neonate and most often in left upper lobe
- Technical issues
- Patient is rotated
- Side to which they are rotated my be more lucent
- Lateral decentering of tube
- Side toward which tube is centered is more lucent
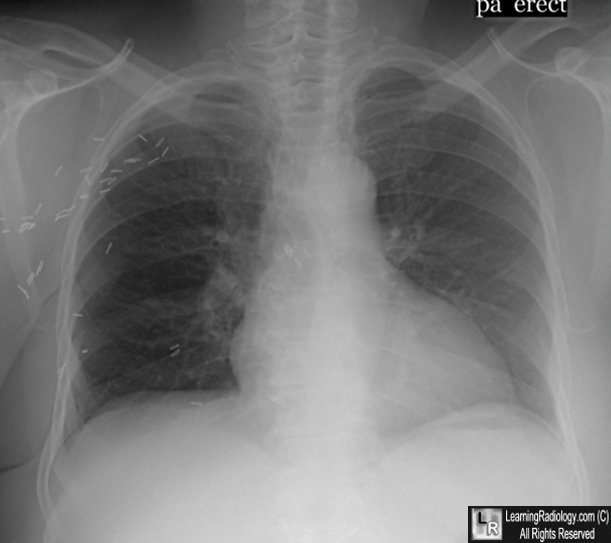
Right Radical Mastectomy. The right hemithorax is more lucent (darker) than the left because the patient had previously undergone a right radical mastectomy in which the breast and the pectoralis muscles were removed. Note the multiple metallic clips from the surgery.
Unilateral Hyperlucent Lung in Children. E Wasilewska, EY Lee and RL Eisenberg. AJR, May 2012, Volume 198, Number 5
|
|
|