
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
© William Herring, MD, FACR

Widespread formation of non-caseatinggranulomas
3:1 female:male
14:1 black:white predominance
ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme)elevated in 70%
SarcoidGeneral

SarcoidGeneral
Kveim skin test
Positive in (70%) but rarely used today
Lofgren Syndrome:
Acute bilateral hilar adenopathy, fever,erythema nodosum and arthralgia
Intrathoracic disease (90%)

SarcoidStage I
Adenopathy alone (43%) - Stage 1
Intrathoracic adenopathy in 80%
Location
Bilateral hilar and (R) paratracheal
Most common (75-90%)
“1-2-3 sign”, “Pawn-broker’s sign”,“Garland sign”

SarcoidStage I
Location
Unilateral hilar nodes rare (3-8%)
Egg-shell calcification hilar nodes in long-standingsarcoid
Rare
DDX: Silicosis

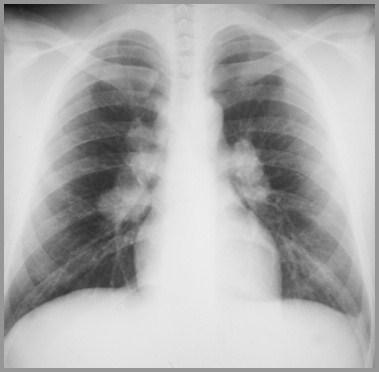
Sarcoid-Stage I-Bilateral Hilar Adenopathy

SarcoidStage II
Adenopathy and parenchymal disease(41%)-Stage 2
Adenopathy usually decreases asparenchymal disease increases
About 1/3 of patients with adenopathydevelop parenchymal disease

Sarcoid-Stage II-Bilateral Hilar Adenopathyand Parenchymal Lung Disease
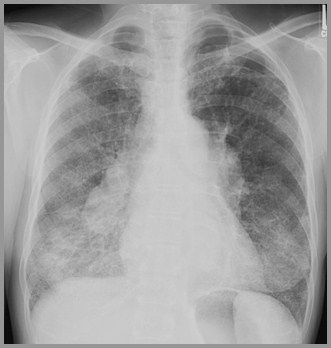

SarcoidStage III
Parenchymal disease alone (30%)
Adenopathy does not developsubsequent to parenchymal disease
If adenopathy develops, think of lymphoma orTB

Sarcoid-Stage III-Parenchymal Lung Diseasewithout Hilar Adenopathy
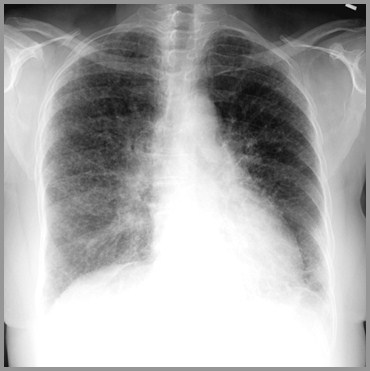

SarcoidStage IV
End-stage lung disease-Stage 4
Diffuse fibrosis
Bronchiectasis-honeycomblung
Multiple cysts

Sarcoid-Stage IV-Diffuse Scarring, CysticDisease and Bronchiectasis
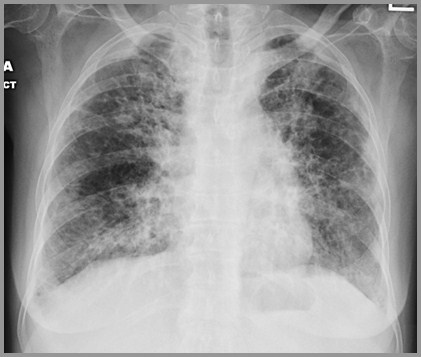

SarcoidPatterns of lung disease
Reticulonodular (46%)
Acinar pattern (20%)
Larger nodules
“Alveolar sarcoid” (2%)
Coalescence of numerous interstitialgranulomas
Air bronchograms present
DDX: Alveolar cell ca, alveolar proteinosis,lymphoma

“Alveolar” Sarcoid
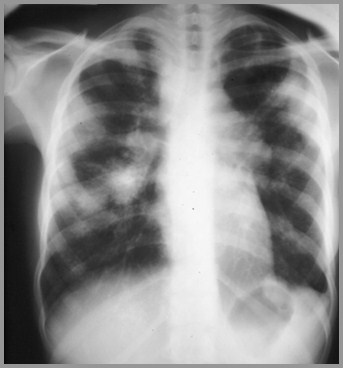

Associated with TB (13%)
Pleural effusion (2%)
Usually exudate with lymphocyticpredominance
Cavitation of nodules (<1%)
Fungus ball formation in chronicsarcoid cavities (usually TB)
Focal pleural thickening
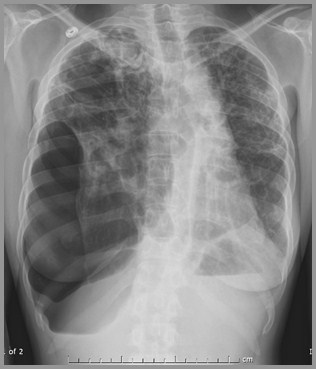
SarcoidUncommon Manifestations

Sarcoid with Bilateral Aspergillomas(Fungus Balls)
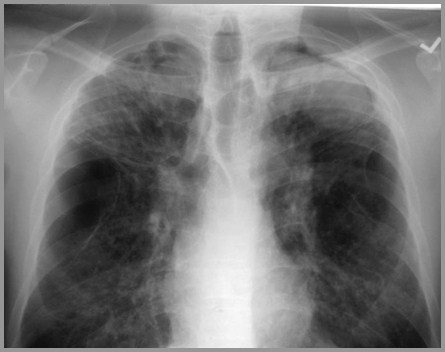

Bronchostenosis with lobar atelectasis
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Cor pulmonale
Pneumothorax 2° chronic lung disease
SarcoidUncommon Manifestations

Sarcoid-Stage IV with Right TensionPneumothorax

Peripheral adenopathy (30%)
Liver
Hepatomegaly
Spleen
Splenomegaly
SarcoidExtrathoracic Disease

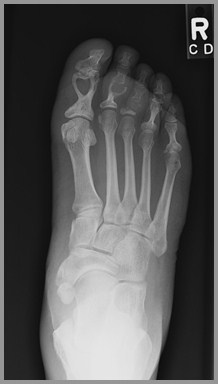
Bone-especially hands
Skin
Erythema nodosum
Lupus pernio (raised purplishnodules)
SarcoidExtrathoracic Disease

Sarcoid of the Foot-Lytic, Punched-outLesions (Heart-shaped)

SarcoidExtrathoracic disease
Muscle
Myopathy
Eyes
Uveitis
Uveoparotid fever
CNS
Granulomatous meningitis
Facial nerve palsy

Myocardium
Arrhythmias
Heart block
Cardiomyopathy
Salivary gland
Parotid enlargement
SarcoidExtrathoracic disease

3/4 show complete resolution of hilaradenopathy
1/3 show complete resolution ofparenchymal disease
20% have irreversible pulmonaryfibrosis
SarcoidPrognosis

The End