
Histiocytosis X
Histiocytosis X
© William Herring, MD, FACR

Histiocytosis XClassification
Letterer-Siwe disease
Hand-Schuller-Christian disease
Eosinophilic Granuloma

Letterer-SiweDisease
Letterer-SiweDisease

Letterer-Siwe DiseaseGeneral
10% of histiocytosis X
Acute disseminated, fulminant form
Age at onset
Several weeks to 2 years
Pathology
May be confused with leukemia

Letterer-Siwe DiseaseClinical
Hemorrhage, purpura
Severe anemia
Fever
Hepatosplenomegaly
Lymphadenopathy
Bone involvement in 50%
Widespread lytic lesions

Letterer-Siwe DiseasePrognosis
70% mortality rate

Hand-Schuller-ChristianDisease
Hand-Schuller-ChristianDisease

Hand-Schuller-ChristianGeneral
15-40% of Histiocytosis X
Age at onset
5-10 years
Pathology
May simulate Ewing'ssarcoma

Hand-Schuller-ChristianClinical
Triad of:
Exopthalmus (33%)
Diabetes insipidus (30-50%)
Lytic skull lesions

Hand-Schuller-ChristianTarget Organs
Bone
Soft tissues
Lung

Hand-Schuller-ChristianBone
Lytic skull lesions with overlying softtissue nodules
Large geographic skull lesions
“Floating teeth” with mandibularinvolvement

Hand-Schuller-ChristianSoft tissue
Hepatosplenomegaly is rare
Common in Letterer-Siwe
Lymphadenopathy may be massive

Hand-Schuller-ChristianLung
Cyst and bleb formation
Spontaneous PTX

EosinophilicGranuloma
EosinophilicGranuloma

Eosinophilic Granuloma
60-80% of Histiocytosis X
Usually confined to bone
Age at onset
5-10 years highestfrequency
Male predominance 3:2

Eosinophilic GranulomaGeneral
Location
Calvarium>mandible>spine>ribs>longbones
Most are monostotic (50-75%)

Eosinophilic GranulomaTarget Organs
Skull50%
Axial skeleton25%
Appendicular skeleton 15%
Lung20%

Eosinophilic GranulomaSkull
Most often diploic space of parietal bone
Round or ovoid punched out lesions withbevelled edge
Bevelled edge=hole-within-a-hole
Sclerotic margin during healing phase
Button sequestrum- bony sequestrumwithin lytic lesion

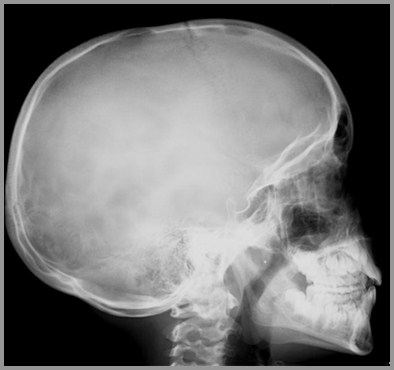
Beveled Edge Lytic Lesion ofEosinophilic Granuloma

Eosinophilic GranulomaAxial Skeleton
“Vertebra plana”-“coin-on-edge”(Calvedisease)=collapse of vertebral body
Mostly thoracic
Most common cause of vertebra plana inchildren

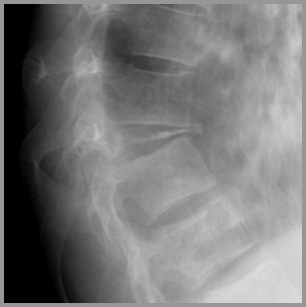
Vertebra plana in EosinophilicGranuloma

Eosinophilic GranulomaAppendicular Skeleton
Expansile, lytic lesion
Mostly diaphyseal
Soft tissue mass
Laminated periosteal reaction

Eosinophilic GranulomaLung
Age peak between 20-40 years
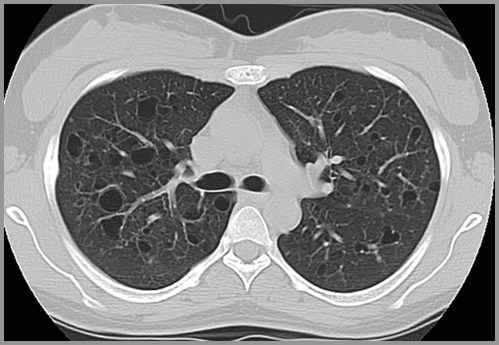
Multiple small nodules
Predilection for apices
Prototype for honeycomb lung
Recurrent pneumothoraces (25%)

Diffuse Reticular Interstitial Disease inEosinophilic Granuloma

Innumerable thin-walled cysts inEosinophilic Granuloma

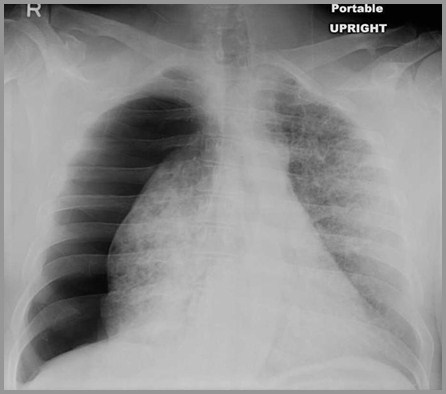
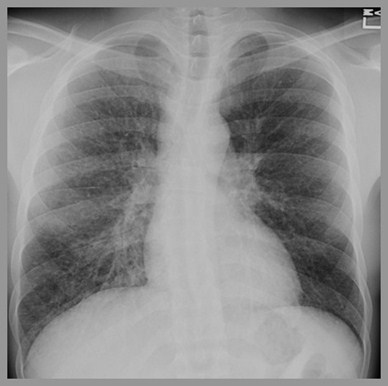
Eosinophilic Granuloma with right-sided tension pneumothorax

Eosinophilic GranulomaNuclear Medicine
Negative bone scans in 35%
Bone lesions usually not Ga-67 avid
Ga-67 may be helpful in detectingnon-osseous lesions

Eosinophilic GranulomaPrognosis
Excellent

The End