
Diseases ofThe Diaphragm
Diseases ofThe Diaphragm
All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Original Authors
© William Herring, MD, FACR

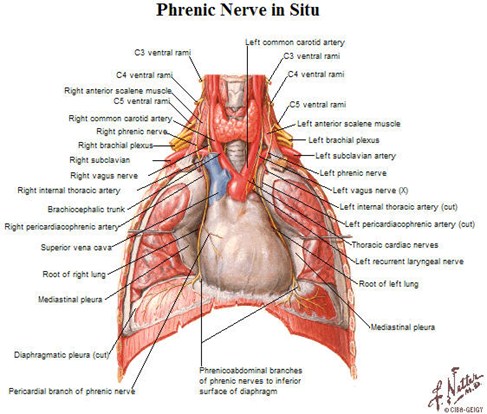
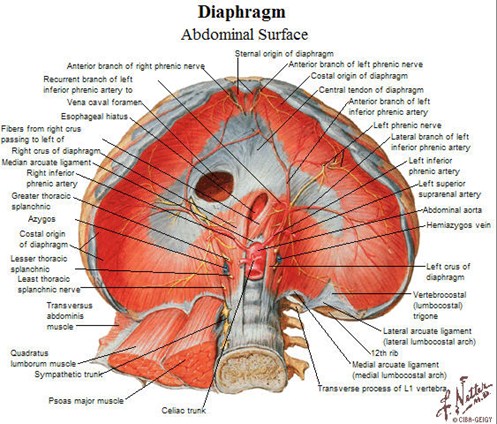
Anatomy of the Diaphragm
Muscle slips attach to 7-12th ribs
Innervated by phrenic n. (C4, C3 and C5)
Central portion is tendinous; outer portionmuscular
Right is 1/2 interspace higher than left in90%
Mean diaphragmatic excursion = 0.8-8.0cm



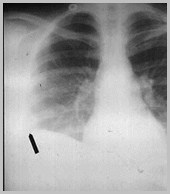
Elevation of theDiaphragm

Elevation of the HemidiaphragmCauses
Subpulmonic effusion
Dome is laterally displaced
Straight edge on lateral at major fissure
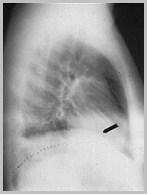

Elevation of the HemidiaphragmCauses
Decreased lung volume
Atelectasis
Hypoplastic lung
Small pulmonary artery, dextrocardia, scimitar vein
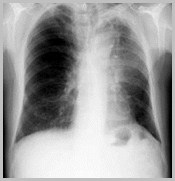
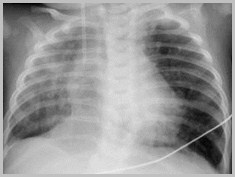

Elevation of the HemidiaphragmCauses
Poor inspiration
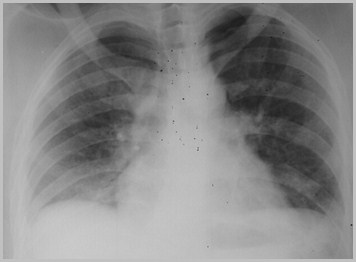

Elevation of the HemidiaphragmCauses
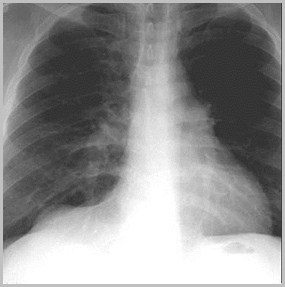
Phrenic NerveParalysis
BrCa
Mets
Iatrogenic-postCABG
Idiopathic
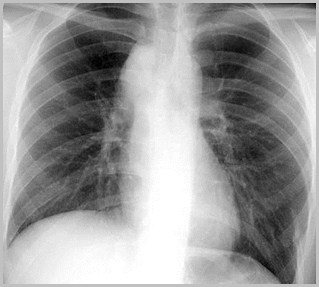



Elevation of the HemidiaphragmCauses
Abdominal Disease
Subphrenic abscess
Right=subhepatic-appendicitis
Left 2° ulcer perforation
Liver mass
Interposition of the colon
Distended stomach
R3
Hepatocellular carcinoma


Elevation of the HemidiaphragmCauses
CongenitalDiaphragmatic Hernia
Traumatic Rupture ofthe Diaphragm
Eventration of theDiaphragm


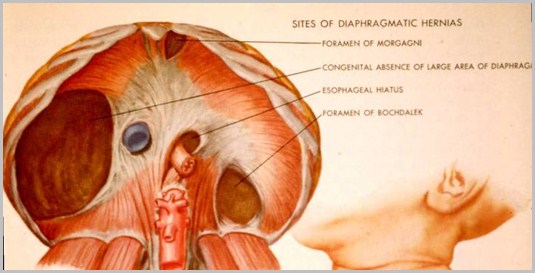
Diaphragmatic HerniasTypes of

CongenitalDiaphragmaticHernias

Congenital Diaphragmatic HerniasGeneral
Absence of closure of pleuroperitoneal fold
9th gestational week
Male to female ratio of 2:1
1:2,000 live births
Left > right 9:1

Congenital Diaphragmatic HerniasAssociated Anomalies
CNS–neural tube defects
GI–malrotation, omphalocoeles
CV
GU
IUGR

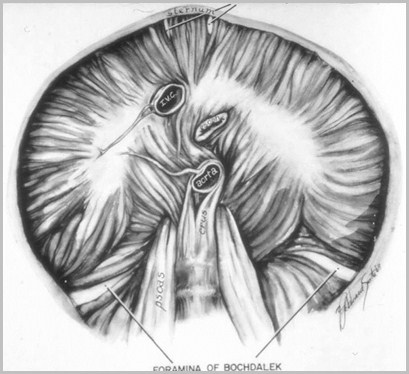
Foramina of Morgagni
Foramina of Bochdalek
Fraser & Pare

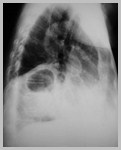
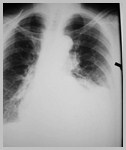
Bochdalek HerniaGeneral
90% of congenital hernias
Posterolateral defect
Abnormality of cephalic fold ofpleuroperitoneal membrane
Left (80%), right (15%), B/L (5%)
Babies–large
Adults–small
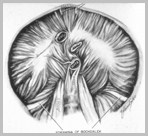

Bochdalek HerniaOrgans Involved
Bowel
Spleen
Fat
Liver (left lobe)
Kidney, pancreas
Stomach

Bochdalek HerniaThe “B’s”
Babies
Back
Big

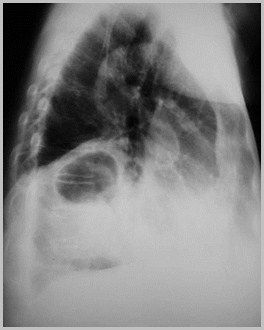
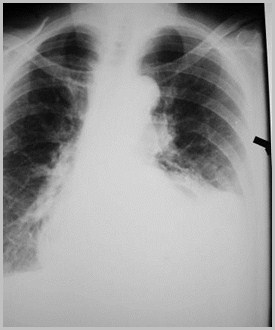
Foramen of Bochdalek Hernia
R3



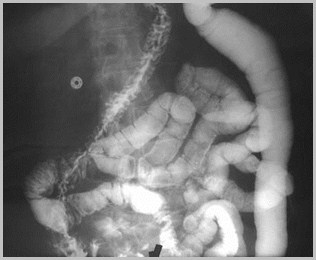
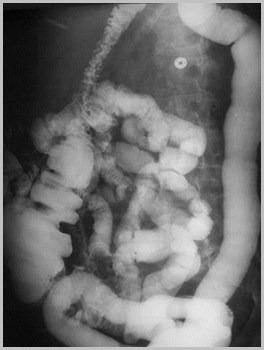
Foramen of Bochdalek Hernia



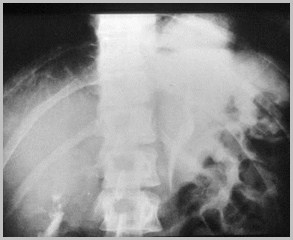
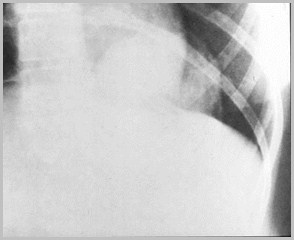
Foramen of Bochdalek Hernia-Kidney
R3



Foramen of Bochdalek Hernia
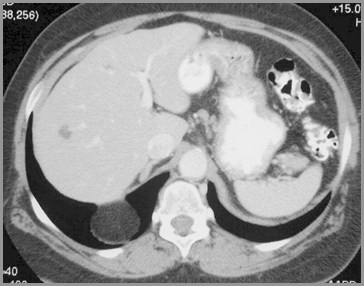

Morgagni HerniaGeneral
Anteromedial parasternal defect (Spaceof Larrey)
Maldevelopment of septum transversum
Overweight, middle-aged, women
Right > left (heart protects)
Associated with
Pericardial defects
Omental fat in pericardial space
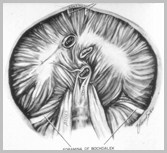

Morgagni HerniaOrgans Involved
Liver
Bowel

Morgagni HerniaThe “M’s”
Middle (anterior and central)
Mature (older children)
Miniscule

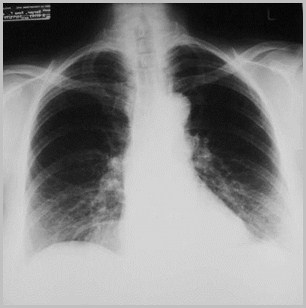
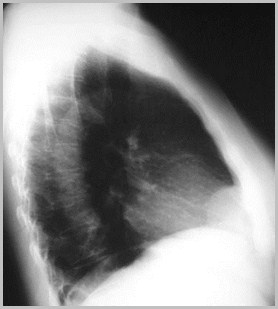
Foramen of Morgagni Hernia


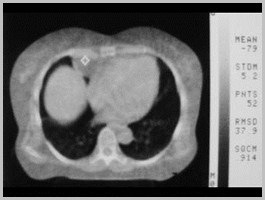
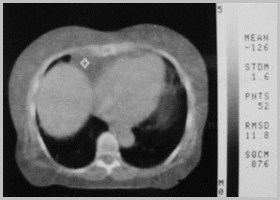
Foramen of Morgagni Hernia


Foramen of Morgagni Hernia
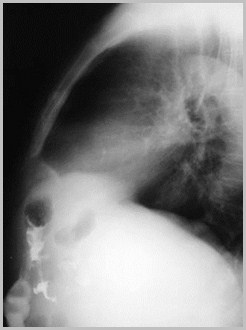
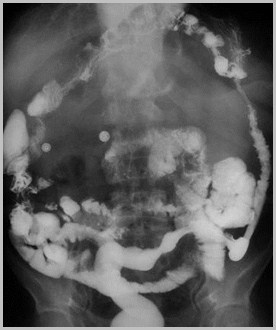



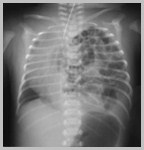
Congenital Absenceof the DiaphragmCongenital Diaphragmatic Hernia

Congenital Absence of DiaphragmGeneral
Delayed onset of hernia may occurfollowing streptococcal infection

Congenital Absence of DiaphragmImaging Findings
Initially, hemithorax may appear opaquebecause loops are fluid-filled
Paucity of bowel loops beneath diaphragm
Once air swallowing begins, multiplelucencies contained within bowel are seen inchest
Respiratory distress may increase as intestineoccupies more of thorax

Congenital Absence of DiaphragmImaging Findings
Some loops may remain fluid-filled
Mediastinal shift to the opposite side
Relative paucity of gas in abdomen
If stomach remains in abdomen, it is morecentrally located than normal

Congenital Absence of DiaphragmPrognosis
Intrathoracic stomach60%
Intra-abdominal stomach6%
Polyhydramnios89%
Operative mortality40-50%
Mortality

Congenital Absence of DiaphragmDDX
Cystic adenomatoid malformation
Staphylococcal pneumonia
Mediastinal cyst

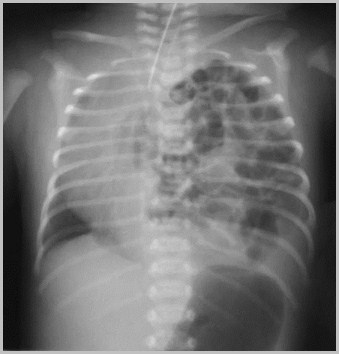
Congenital Absence of the Diaphragm


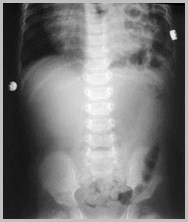
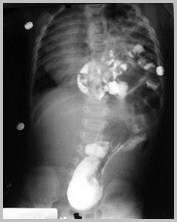
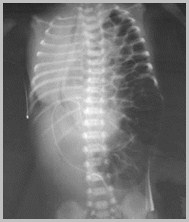
Congenital Absence of the Diaphragm
R3

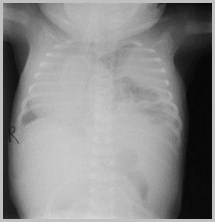
Congenital Absence of the Diaphragm
R3


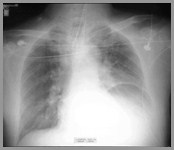
DiaphragmaticRupture
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia

Diaphragmatic RuptureEtiology
Blunt trauma (5–50%)
2° increased intra-abdominal pressure
MVA
Fall from height
Penetrating trauma (50%)
Knife, bullet

Diaphragmatic RuptureGeneral
5% of all diaphragmatic hernias
Most (90%) are left-sided
Central and posterior >10cm in length
Contain stomach, colon, small bowel,omentum, spleen
Half have no initial abnormal radiographicfindings
Half are missed clinically

Diaphragmatic RuptureGeneral
Associated with
Fx ribs
Pneumoperitoneum
Ruptured spleen
Delayed diagnosis = higher mortality
MRI most useful in showing site of tear

Diaphragmatic RuptureImaging Findings
Air/fluid levels in left hemithorax
Contralateral shift of heart andmediastinal structures
Absence of bowel in abdomen
NGT in left hemithorax
“Pinch-cock” “hourglass” configuration
MRI shows diaphragm in all planes

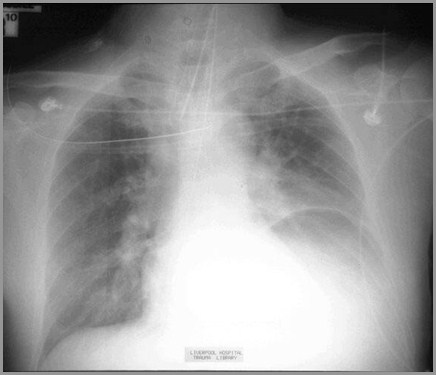
Diaphragmatic Rupture

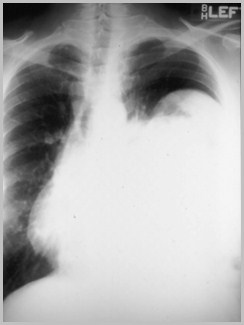
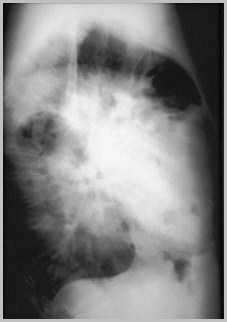
Diaphragmatic Rupture

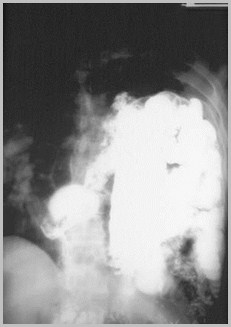

Diaphragmatic Rupture

Traumatic Diaphragmatic HerniaComplications
Strangulation of bowel
Hydrothorax/hemothorax 2° strangulation

Hiatal Hernia

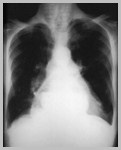
Hiatal HerniaGeneral
Most common form of diaphragmatichernia in adult
Air/fluid level(s) in “mass” posterior toheart
May contain entire stomach
Can lead to volvulus
Usually projects to left of spine

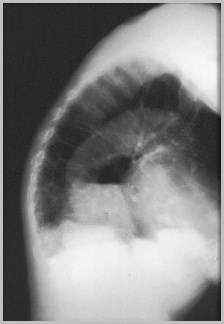
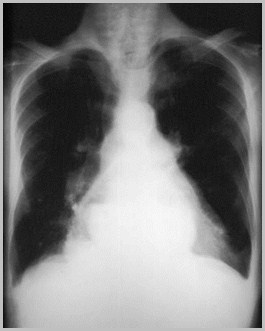
Hiatal hernia



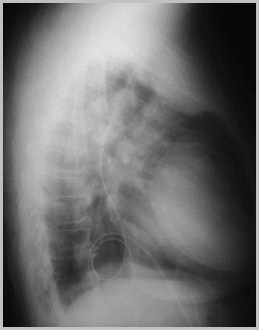
Hiatal hernia



Eventration of theDiaphragm

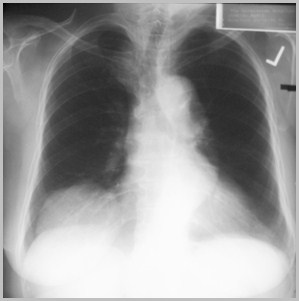
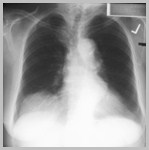
Eventration of the DiaphragmGeneral
Congenitally thin muscular portion ofhemidiaphragm
Still, incidence increases with age
Anteromedial on right
R:L 5:1
When on left, usually whole hemidiaphragm


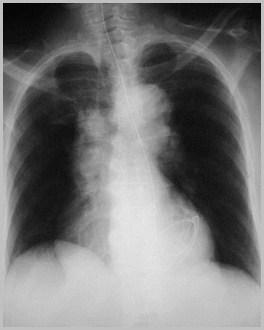
Eventration right hemidiaphragm



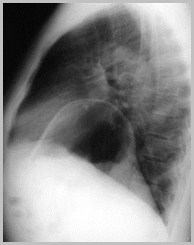
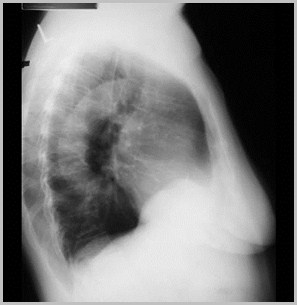
Eventration left hemidiaphragm
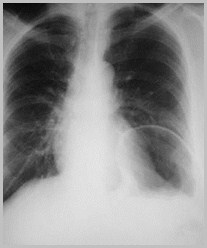



Paralysis of theDiaphragm

Paralysis of the Hemidiaphragm
Most often from phrenic nerve involvement
Neoplasms, CABG surgery (2° ice)
Idiopathic
Males, right hemidiaphragm
Sniff test
Paradoxical upward motion on affected side

Phrenic Nerve Paralysis
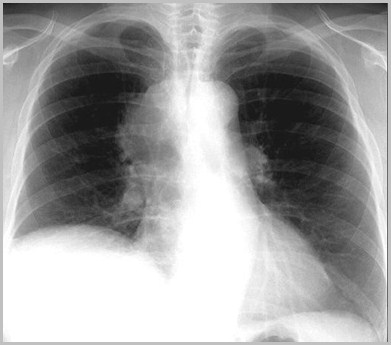
R3

Sniff Test
Normal excursion of 1-2 ribs
Breathe in, diaphragm down
Breathe out, diaphragm up
Paralyzed – paradoxical motion
Breathe in, diaphragm up
Breath out, diaphragm down
Useless with large effusion

Sniff Test
Paralysis of the hemidiaphragmversus eventration
Diaphragmatic motion is paradoxical inparalysis but not with eventration

Bilateral Paralysis of the Diaphragm
Less common than unilateral
Occurs in neurologic disease, syrinx, MS
Most develop respiratory failure andhypercapnea

Tumors of the Diaphragm
Very rare
Benign vs. malignant 50:50
Lipoma (most common benign)
Fibrosarcoma (most common malignant)
Mets occur via direct extension frompleura or lung

Side Preference-Hernias
Type of hernia
More common on ___ side
Bochdalek hernia
Morgagni hernia
Traumatic rupture
Eventration
Left
Right
Left
Right

“Hernias”
Cong.Absence
Rupture
Eventration
HH
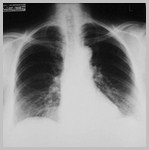
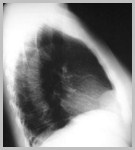
Bochdalek
Morgagni

The End