
An Approach to Arthritis
William Herring, MD, FACR

Definition
Disease that affects bones on bothsides of the joint space and
Narrows the space in between them

Arthritis or Not
AVN
DJD
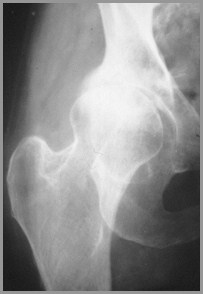
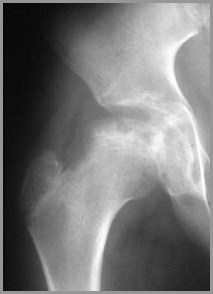

Arthritis or Not
PVNS
DJD

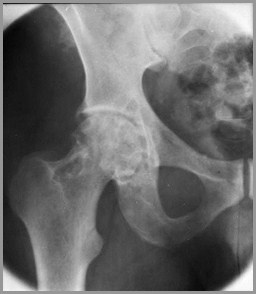

Classification
Hypertrophic
Hallmarks
Bone production
Sclerosis
Infectious
Hallmark
Destruction of articular cortex
Erosive
Hallmark
Erosions

Hypertrophic Arthritis
Degenerative arthritis
Primary
Secondary
Charcot arthropathy

1º Degenerative Arthritis
Intrinsic degeneration of articularcartilage
Excessive wear and tear
Most commonly hips and knees
Less commonly shoulders and elbows

1º Degenerative Arthritis
X-ray Findings
Narrowing of joint space
Subchondral sclerosis
Marginal osteophyte formation
Subchondral cysts

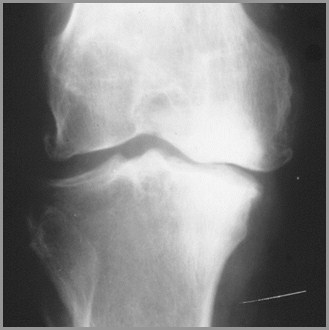
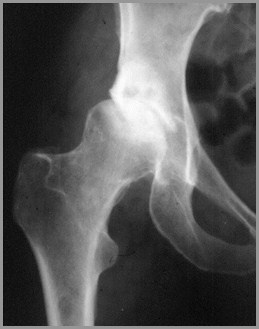
1º DJD of knees affects medial,weight-bearing surface
1º DJD of hips affects superior,weight-bearing surface

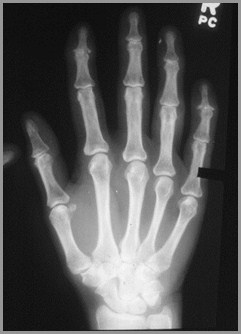
1º Degenerative ArthritisHands
Not due to mechanical stress
F:M 10:1
Most often involves DIP joints
Sclerosis
Marginal osteophyte formation
1st MCP joint of thumb

1º DJD of Hands

2º Degenerative Arthritis
Another process destroys articularcartilage
Degenerative changes supervene
How to recognize
Atypical age (DJD in 20 year-old)
Atypical appearance (Marked DJD of 1 hip)
Atypical locations (CPPD and knee)

2º Degenerative ArthritisCauses
Trauma
Infection
Avascular necrosis
CPPD
RA
Hemophilia
Bottom line: Any arthritis →DJD

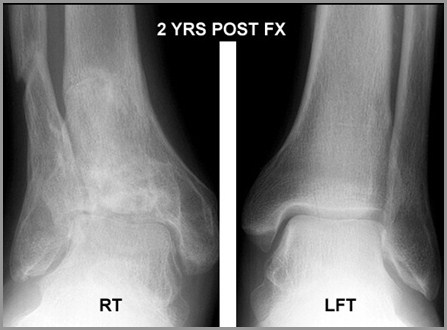
2º DJD of right ankle following fracture

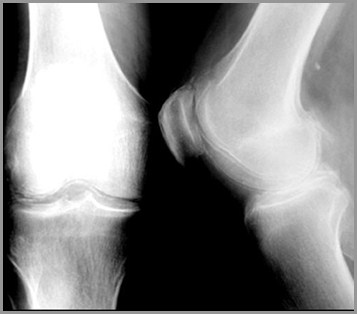
Calcium PyrophosphateDeposition Disease (CPPD)
May be idiopathic or associated with
Hyperparathyroidism, hemochromatosis
Symmetric involvement: knees (mostcommon), wrists, MCPs
Sudden onset of pain and fever
Clinically
Tender, swollen, red, LOM

CPPDFindings
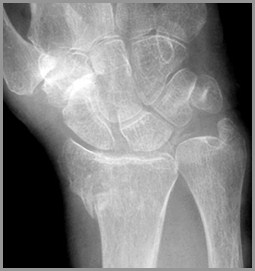
Calcification of articular cartilage
Knee, hip, shoulder
Triangular fibrocartilage of ulna
Symphysis
Large subchondral cysts
Preferential involvement of femero-patellar compartment

CPPD

Hypertrophic ArthritisClassification
Degenerative arthritis
Primary
Secondary
Charcot arthropathy

Charcot’s ArthropathyGeneral
Disturbance in sensation leads tomultiple microfractures
Pain sensation intact from muscles andsoft tissue
Causes
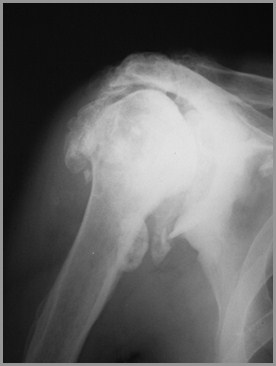
Shoulders – syrinx, spinal tumor
Hips – tertiary syphilis, diabetes
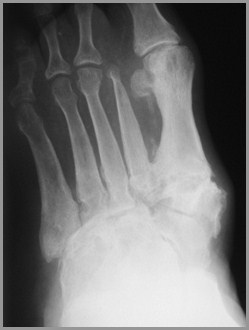
Feet – diabetes

Charcot’s ArthropathyFindings
X-ray findings
Fragmentation
Soft tissue swelling
Destruction of joint
Sclerosis
Osteophytosis

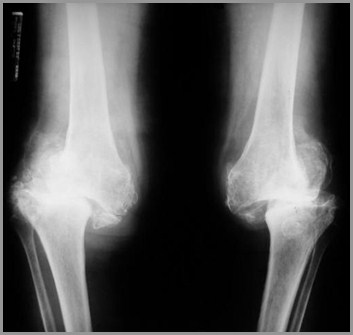
Charcot’s Knees-Diabetes

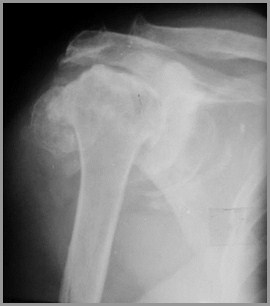
Charcot’s Shoulder - Syrinx

Charcot’s Arthropathy of Foot -Diabetes

Classification
Hypertrophic
Hallmarks
Bone production
Sclerosis
Infectious
Hallmark
Destruction of articular cortex
Erosive
Hallmark
Erosions

Infectious Arthritis
More common in adults
Usually from local trauma-surgery or accident
Children get osteomyelitis
Destruction of articular cartilage & cortex
Tends to affect one joint
Fingers from human bites
Feet from diabetes
Hips from THRs

Normal articular cortex
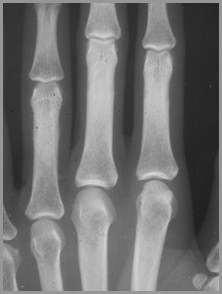
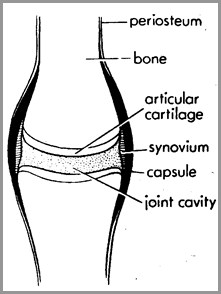
Normal joint

Infectious ArthritisCauses
Usually staph - “early” destruction ofarticular cortex
Rapid course (unlike most arthritides)
TB spreads via bloodstream from lung
More protracted course
In children, spine most common; in adults, knee
Severe osteoporosis
Healing with ankylosis common in both

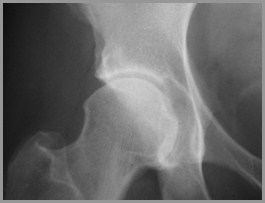
Septic arthritis of hip withpathologic fracture
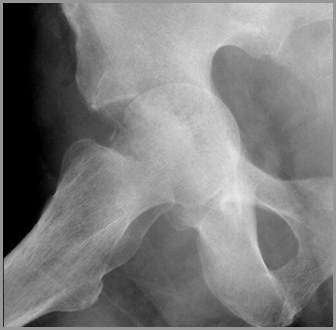
Normal hip
Normal acetabular white line

Septic arthritis of toe
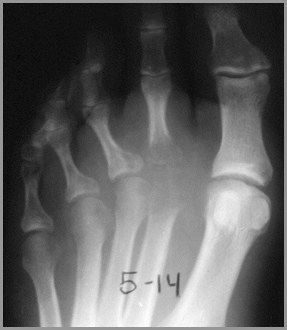

TB septic arthritis over 1 year
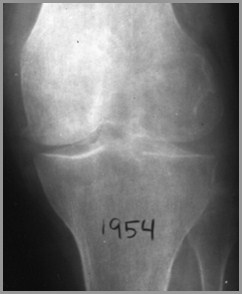
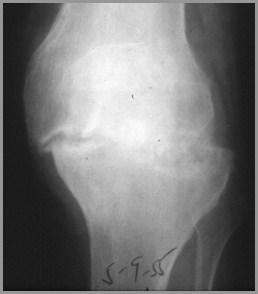
1982
1983

ClassificationErosive Arthritis
Hypertrophic
Hallmarks
Bone production
Sclerosis
Infectious
Hallmark
Destruction of articular cortex
Erosive
Hallmark
Erosions

Erosive ArthritisGeneral
Synovial proliferation(pannus formation)
Inflammation
Erosions seen in smalljoints (hands) better thanlarge (hips)
Destroy portion of cortex
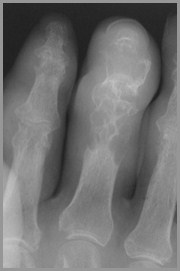

Erosive ArthritisTypes
Rheumatoid arthritis
Gout
Hemophilia
Erosive osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid variants
Ankylosing spondylitis
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies
Psoriatic arthritis
Reiter's
Inflammatory bowel disease

Connective tissue disease
Scleroderma
SLE
Jaccoud's arthropathy
Sarcoidosis
Rare
Amyloid
Erosive ArthritisMore Types

Rheumatoid ArthritisGeneral
Bilaterally symmetrical
Earliest change: STS MCP, PIP, ulnar styloid
Radiocarpal jt most commonly narrowed
Periarticular demineralization
Begins MCP jts of 1st and 2nd fingers
Large joints usually no erosions

Rheumatoid ArthritisGeneral
Can lead to 2º DJD
Marked narrowing of joint space with intactarticular cortex, think of RA
Little or no sclerosis
Especially, hips and knees

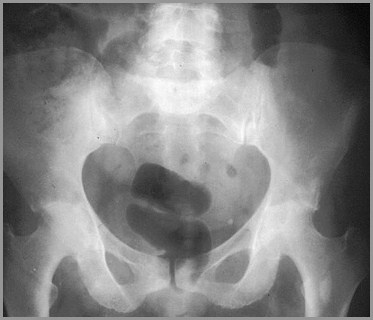
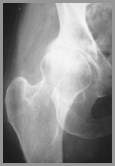
RA of Hips – Marked narrowing, littlesclerosis

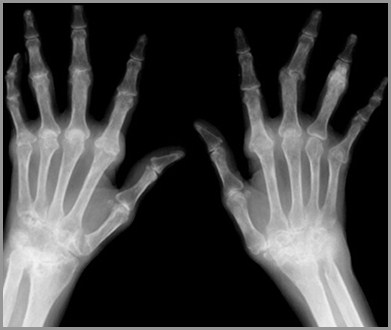
RA Hands

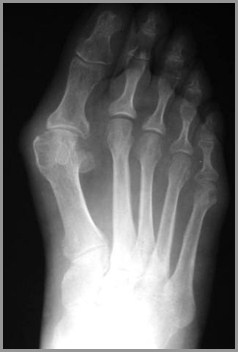
RA of Foot
RA usuallyinvolves 5thMT-P jointfirst

GoutGeneral
Long latent period between onset ofsymptoms and bone changes
Asymmetric and monoarticular
More common in males
Most common at 1st MT-P joint
Tophi rarely calcify
Olecranon bursitis is common

GoutFindings
Juxta-articular erosions
Sharply marginated with sclerotic rims
Overhanging edges (“rat-bites”)
No joint space narrowing until later
Little or no osteoporosis
Soft tissue swelling
Tophi not calcified

Gout
R3
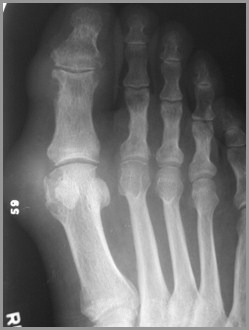

Gout
R3
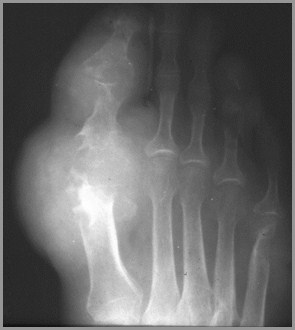

HemophiliaGeneral
Usually seen in large joints
Hemorrhage produces synovitiswhich leads to pannus
Incites hyperemic response
Bone resorption and remodeling
Especially in open epiphyses
DDx: JRA

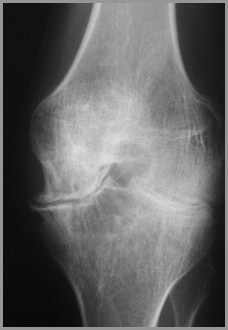
HemophiliaFindings
Overgrowth of epiphyses
Resorption of secondary trabeculae
Longitudinal striations
Widening of interconylar notch of knee
Joint effusion
Hemosiderin deposit around joint

Hemophiliac Arthropathy

Erosive Osteoarthritis
Post-menopausal females
Changes like DJD but with markedinflammation and erosions
IP joints of hands and carpal-MCP jointof thumb
DDx: Psoriasis (skin changes)

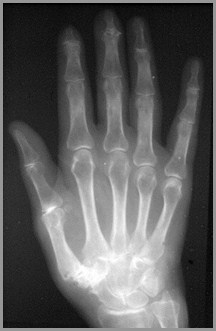
Erosive Osteoarthritis

Rheumatoid VariantsGeneral
Negative Rheumatoid Factor
Positive HLA-B27
Differ from RA by
Osteoporosis usually absent in variants
Periostitis (whiskering) frequent
Ankylosis more common
Asymmetric peripheral joint changes

Psoriatic Arthritis
Almost always accompanies skindisease, especially nail changes
Involves DIP joints of hands > feet
Cup-in-pencil deformity
Resorption of terminal phalanges
No osteoporosis

Psoriasis of hands
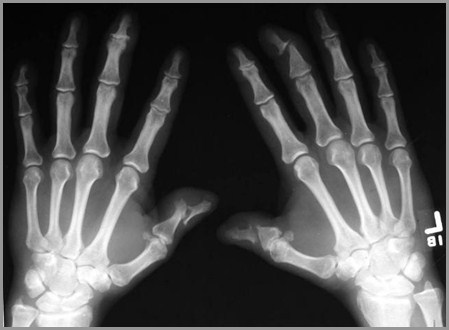

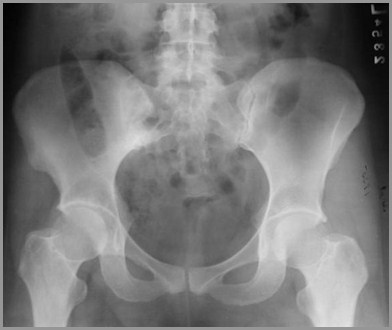
Psoriatic SacroiliitisLike Inflammatory Bowel Dz and Reiter’s - producesB/L but asymmetric SI joint involvement

Psoriasis of SpineNon-marginal syndesmophytes
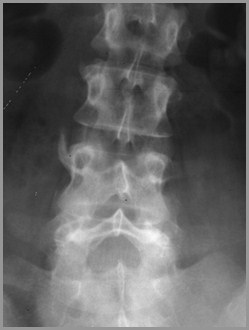
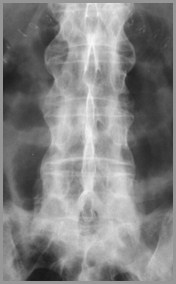
AS

Reiter’s Syndrome
Urethritis, arthritis (50%) & conjunctivitis
Periostitis at sites of tendinous insertion
Whiskering
Like DISH, ankylosing spondylitis
Affects feet more than hands; also SI jt
Resembles RA
Reiter’s also has osteoporosis

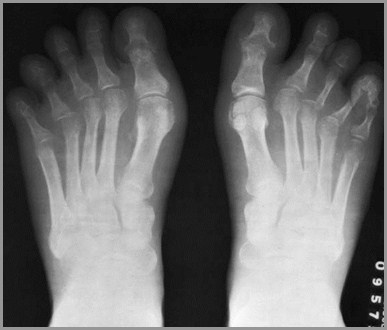
Reiter’s Syndrome
R3

Ankylosing Spondylitis
HLA-B27 positive
B/L SI arthritis
Squaring of vertebral bodies
Bamboo-spine from continuoussyndesmophytes
Peripheral large joint erosive arthritis

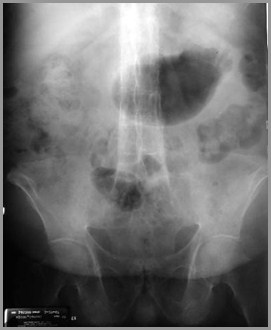
Ankylosing Spondylitis

Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Can occur with either Crohn’s or UC
More common with UC
Looks like AS in spine
B/L asymmetric sacroiliitis
Like psoriasis
Peripheral joint STS without erosions

Overview
Hypertrophic – sclerosis & bone production
Degenerative Arthritis
Primary
Secondary
Charcot Arthropathy
Infectious – destruction articular cortex
Pyogenic
Tuberculous

Overview
Erosive - erosions
RA
Gout
Hemophilia
Erosive osteoarthritis
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Psoriatic arthritis
Reiter’s Syndrome

Unknowns

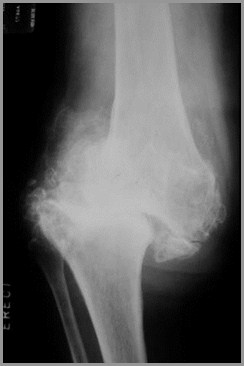
Charcot Arthropathy

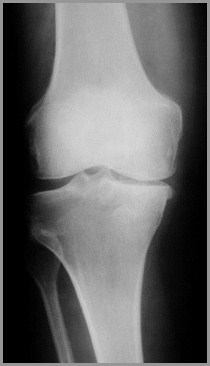
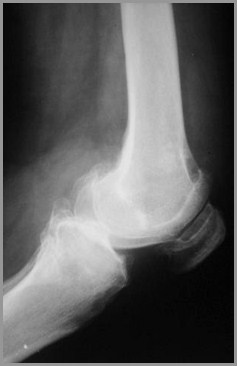
Degenerative Arthritis

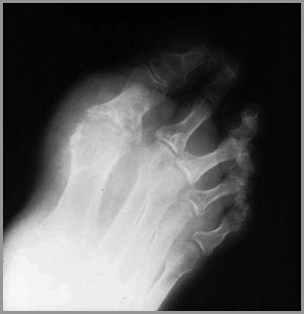
Gout

Septic Arthritis
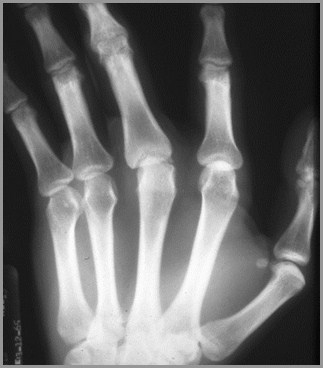

Rheumatoid Arthritis
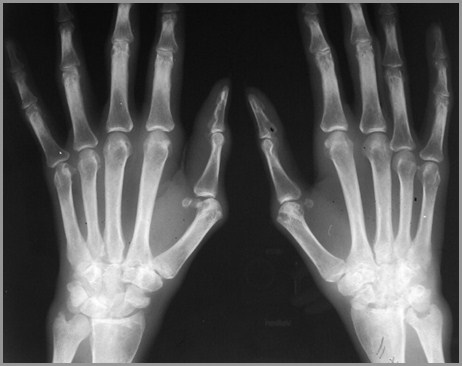
R
L

Secondary DJD-Trauma
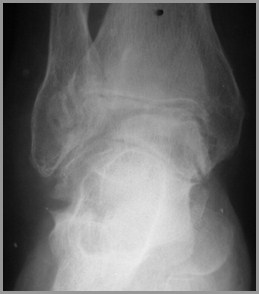
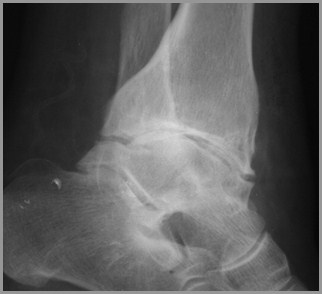

Gout
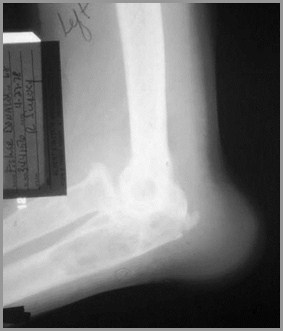

CPPD
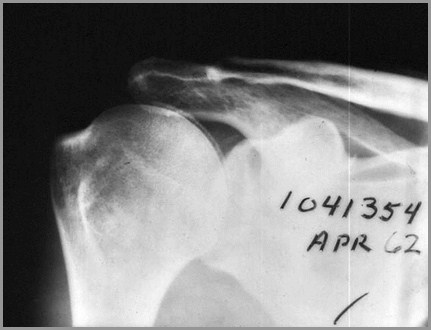

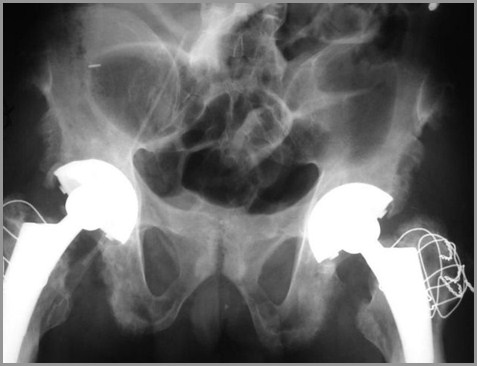
Ankylosing Spondylitis

Charcot of Hip
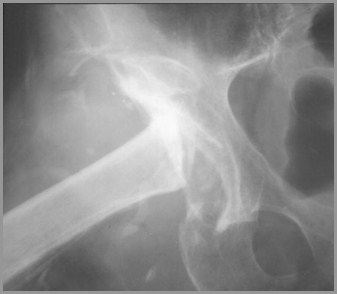

Degenerative Arthritis
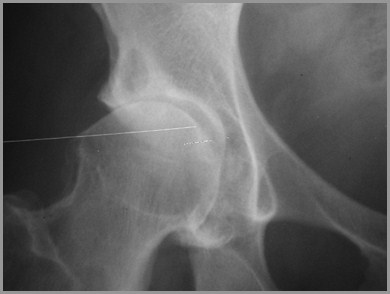

Hemophilia
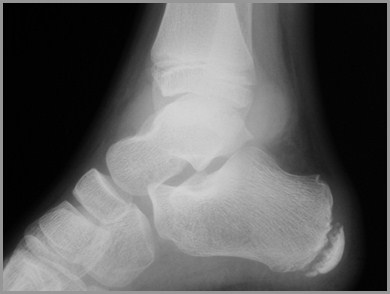

Rheumatoid Arthritis
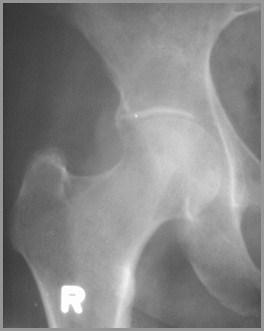

Charcot Arthropathy

The End