|
|
Lipohemarthrosis
- Mixture
of fat and blood in joint capsule following trauma
- Lipohemarthroses
occur in approximately 40% of all intra-articular fractures of the knee
- May
take up to 3 hours after trauma to appear
- Gravity
and a period of rest are needed to depict fluid-fluid layer which is
characteristic of lipohemarthrosis
- Fat
and blood enter joint from marrow space through an osteochondral defect at
articular surface of joint
- Fat
is less dense than blood so fat floats on the surface with the heavier,
denser blood beneath it
- Can
only be seen with a horizontal x-ray beam (beam is parallel to the floor)
- CT and
MRI have been used to diagnose lipohemarthrosis
- Also
to identify occult fractures not detected by radiography
- Lipohemarthrosis
is not seen in all cases of intracapsular fracture
- Presence
of a fat-fluid level is nearly diagnostic of a fracture, even when that
fracture is radiographically occult
- Knee
joint
- Most
commonly, lipohemarthroses are produced with minimally displaced
fractures of the tibial plateau
- Since
cross-table lateral views of the knee in which the x-ray beam is
horizontal are commonly performed in trauma patients, lipohemarthroses
are more commonly seen with this joint
- Three
bands can normally be distinguished
- The
top band consists of fatty material
- The
next band below is composed of serum and serous joint effusion
- Cellular
parts of blood, i.e., erythrocytes and leukocytes settle to the bottom
layer due to gravity
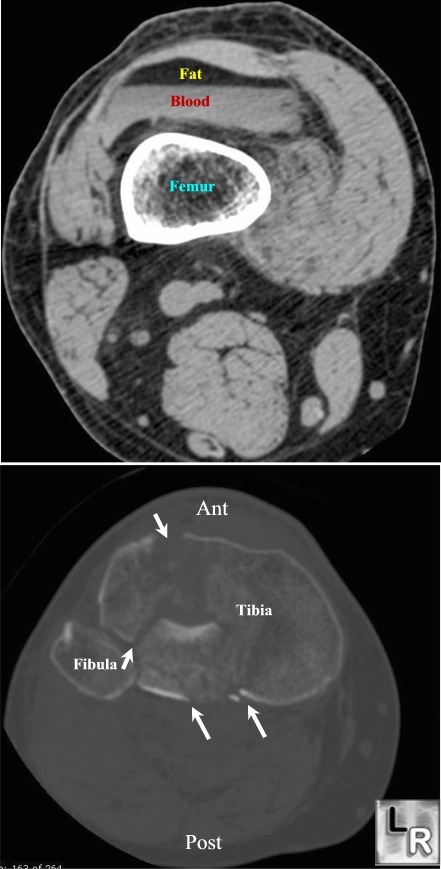
Lipohemarthosis. Upper image shows fat floating atop blood in the knee
joint;
the lower image demonstrates a markedly comminuted fracture of the
proximal tibia (white arrows) from which the marrow entered the joint
The CT, MRI, and
Radiographic Appearance of Lipohemarthrosis Sorenson SM, Wolfson K, Gentili A,
Masih S, Seeger LL UCLA School of
Medicine AJR On-Line
Lipohemarthrosis
of the knee: specific imaging findings Christoph Schick · Martin G. Mack ·
Ingo Marzi · Thomas J. Vogl European
Radiology
|
|
|