|
Aortic Dissection
Dissecting Aortic Aneurysm
- 3:1
male to female predominance
- Over
the age of 40
- Hemorrhage
in the media (at vasa vasorum) leading to either
- Tear
in the weakened intima which breaks into the lumen, or
- Hemorrhage
in the wall (less common)
- Hemorrhage
separate media from adventitia
· Predisposing
factors
o
Hypertension
(most commonly)
o
Atherosclerosis
o
Cystic
medial necrosis
§
Marfan’s syndrome
o
Coarctation
of the aorta
o
Aortic
stenosis
o
S/P
prosthetic aortic valve
o
Trauma
(rare)
o
Pregnancy
(rare)
· Aneurysm
defined by size criteria
o
In
general, ascending aorta > 5 cm
o
Descending aorta > 4 cm
·
Vessels
involved with dissection
o
Any
artery can be occluded
o
Usually
the right coronary and three arch vessels are involved with arch aneurysms
o
Right
pulmonary artery and left-sided pulmonary veins may be occluded
· Types
o
DeBakey
Type I
§
Involves entire aorta
o
DeBakey
Type II
§ Least common
·
Ascending aorta only
o
DeBakey
Type III
§ Most common
·
Descending aorta only
o
Stanford
Type A
§ Ascending aorta involved
·
Over half develop aortic regurgitation
o
Stanford
Type B
§ Ascending aorta NOT involved
·
Most dissections arise either just distal to the
aortic valve or just distal to aortic isthmus
· True versus false channel
o
False
channel usually arises anterior in the ascending aorta and spirals to posterior
and left lateral in descending aorta
o
True
channel is usually larger
o
Slower
flow in false channel on MR
DeBakey Classification
|
Stanford Classification
|
Portion of Aorta Involved
|
Common causes
|
RX
|
DeBakey Type I
|
Stanford Type A
(ascending aorta involved)
|
Involves entire aorta
|
Hypertension
Atherosclerosis
|
Usually surgically*
|
DeBakey Type II
(least common)
|
Stanford Type A
(ascending aorta involved)
|
Ascending aorta only
|
Cystic medial necrosis
e.g. Marfan’s
Ehlers-Danlos
|
Usually surgically*
|
DeBakey Type III
(most common)
|
Stanford Type B
|
Descending aorta only
|
Hypertension
Atherosclerosis
|
Usually medically
|
*Goal is to prevent
backward involvement of the aortic valve or rupture into pericardium
·
Clinical
o
Sharp,
tearing, intractable chest pain
o
Murmur
or bruit of aortic regurgitation
o
Previously
hypertensive, now possible shock
o
Asymmetric
peripheral pulses
o
Pulmonary
edema
·
Imaging
Findings
o
Chest
films
§
Mediastinal widening
§
Left paraspinal stripe
§
Displacement of intimal calcifications
§
Apical pleural cap
§
Left pleural effusion
§
Displacement of endotracheal tube or nasogastric
tube
o
MRI
§
Intimal flap
§
Slow flow or clot in false lumen
o
CT
§
Intimal flap
§
Displacement of intimal calcification
§
Differential contrast enhancement of true versus
false lumen
o
Angiography
§
Intimal flap
§
Double lumen
§
Compression of true lumen by false channel
§
Increase in aortic wall thickness > 10 mm
§
Obstruction of branch vessels
·
DX
o
MRI
if available is usually best for imaging ascending aorta
o
Contrast-enhanced
CT can image arch and descending aorta
o
Transesophageal
ultrasound, if available, especially for root and ascending aorta
o
Angiography
· Prognosis
Timing
|
Death
|
Immediate
|
3%
|
Within 24 hours
|
20-30%
|
By end of 1st week
|
50%
|
By 3 weeks
|
60%
|
By 3 months
|
80%
|
Alive at 1 year
|
10-20%
|
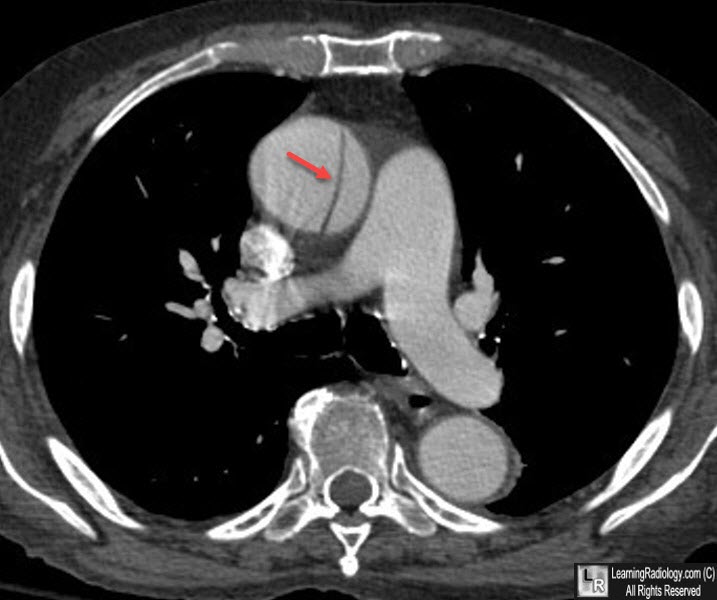
CT of abdominal aorta show intimal flap (dark line)
with true lumen anteriorly and false lumen posteriorly
|